Introduction
Machine learning (ML) is a field of artificial intelligence that enables computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions. This post covers the foundational concepts, key algorithms, and deep learning techniques every practitioner should know.
Types of Machine Learning
Supervised Learning
Supervised learning uses labeled data to train models. The algorithm learns to map inputs \(( X )\) to outputs \(( Y )\) by minimizing a loss function. Common tasks: classification and regression.
Example: Email spam detection, house price prediction.
Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning works with unlabeled data. The goal is to find patterns or groupings in the data.
Example: Customer segmentation, dimensionality reduction.
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning trains an agent to make a sequence of decisions by rewarding desired behaviors and punishing undesired ones. The agent learns a policy \(( \pi(a|s) )\) to maximize cumulative reward.
Example: Game playing (AlphaGo), robotics.
Key Concepts
Bias-Variance Tradeoff
- Bias: Error from erroneous assumptions in the learning algorithm.
- Variance: Error from sensitivity to small fluctuations in the training set.
A good model balances bias and variance to minimize total error:
\[\text{Total Error} = \text{Bias}^2 + \text{Variance} + \text{Irreducible Error}\]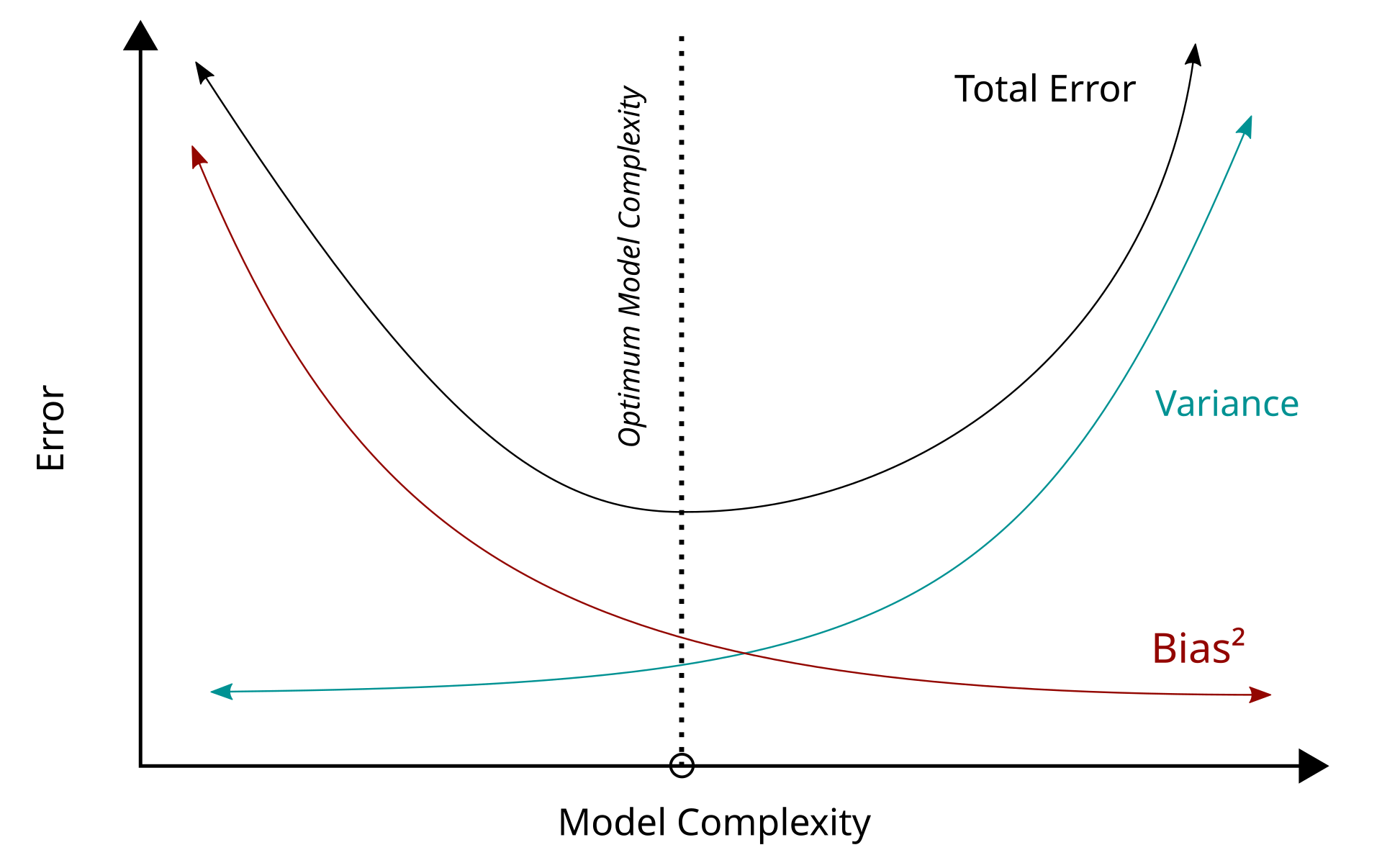
Overfitting and Prevention
- Overfitting: Model learns noise in the training data, performing poorly on new data.
- Prevention: Use regularization (L1/L2), cross-validation, simpler models, or more data.
Cross-Validation
Cross-validation splits data into training and validation sets multiple times to ensure the model generalizes well. The most common is k-fold cross-validation.
Diagram: Insert a diagram showing k-fold data splits.
Precision, Recall, F1-Score
- Precision: \(( \frac{TP}{TP + FP} )\) — How many predicted positives are correct?
- Recall: \(( \frac{TP}{TP + FN} )\) — How many actual positives are captured?
- F1-Score: Harmonic mean of precision and recall.
When to prioritize:
- Precision: When false positives are costly (e.g., spam detection).
- Recall: When false negatives are costly (e.g., disease screening).
Core Algorithms
Linear Regression
Linear regression models the relationship between a dependent variable \(( Y )\) and one or more independent variables \(( X )\):
\[\hat{y} = w^T X + b\]Assumptions: Linearity, independence, homoscedasticity, normality of errors.
Decision Trees
Decision trees split data based on feature values to make predictions. They handle non-linear data and are easy to interpret.
k-Means Clustering
k-means partitions data into k clusters by minimizing within-cluster variance. Intuition: Assign points to the nearest centroid, then update centroids.
SVM vs. Logistic Regression
- SVM: Finds the hyperplane that maximizes margin between classes. Can use kernels for non-linear separation.
- Logistic Regression: Models probability of class membership using the logistic function.
Curse of Dimensionality
As the number of features increases, data becomes sparse, making learning and visualization harder. Distance metrics lose meaning in high dimensions.
Deep Learning
What is a Neural Network?
A neural network is a collection of interconnected nodes (neurons) organized in layers. Each neuron computes a weighted sum of its inputs, applies an activation function, and passes the result to the next layer.
Forward and Backpropagation
- Forward propagation: Compute outputs layer by layer.
- Backpropagation: Compute gradients of the loss with respect to weights using the chain rule, then update weights.
Gradient Descent
An optimization algorithm that updates model parameters in the direction of the negative gradient of the loss function: \(\theta \leftarrow \theta - \eta \nabla_\theta J(\theta)\) Where \(( \eta )\) is the learning rate.
Activation Functions
Introduce non-linearity. Common choices:
- Sigmoid: \(( \sigma(x) = \frac{1}{1 + e^{-x}} )\)
- ReLU: \(( \max(0, x) )\)
- Tanh: \(( \tanh(x) )\)
Loss Functions
Measure the difference between predictions and true values. Examples:
- MSE for regression: \(( \frac{1}{n} \sum (y_i - \hat{y}_i)^2 )\)
- Cross-entropy for classification.
Deep Learning Architectures & Techniques
CNNs, RNNs, Transformers
- CNNs: Good for images; use convolutional layers to extract spatial features.
- RNNs: Good for sequences; maintain hidden state across time steps.
- Transformers: Use self-attention to model relationships in sequences; state-of-the-art for NLP.
Batch Normalization
Normalizes layer inputs to stabilize and speed up training.
Dropout
Randomly sets a fraction of activations to zero during training to prevent overfitting.
Transfer Learning
Fine-tune a pre-trained model on a new task. Useful when labeled data is scarce.
Attention Mechanism
Allows the model to focus on relevant parts of the input sequence. Key in transformer models.
Training & Optimization
Epochs, Batches, Iterations
- Epoch: One pass through the entire dataset.
- Batch: Subset of data processed before updating weights.
- Iteration: One update step (one batch).
Learning Rate
Controls the step size in gradient descent. Too high: may diverge. Too low: slow convergence.
Gradient Clipping
Limits the magnitude of gradients to prevent exploding gradients, especially in RNNs.
Vanishing/Exploding Gradients
- Vanishing: Gradients become too small; network stops learning.
- Exploding: Gradients become too large; weights diverge.
- Solutions: Use ReLU, batch norm, gradient clipping, or residual connections.
Scenario-Based & Applied Questions
Ranking Instagram Posts
Design a deep learning model (e.g., using a neural network with user, post, and engagement features) to predict a relevance score for each post. Use ranking loss (e.g., pairwise hinge loss) and evaluate with metrics like NDCG.
Fraud Detection
Use supervised learning (e.g., random forest, neural network) on transaction features. Address class imbalance with techniques like SMOTE or class weighting. Evaluate with precision, recall, and ROC-AUC.
Explaining Deep Learning to Non-Technical Stakeholders
“Deep learning models learn patterns from large amounts of data, similar to how humans learn from experience. They can recognize images, understand speech, or make recommendations by finding complex relationships in the data.”
Evaluating Face Recognition
Use metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and ROC-AUC. For real-world systems, also consider false acceptance rate (FAR) and false rejection rate (FRR).